Artificial technology (AI) technology is reshaping the ways we interact, learn and innovate, and healthcare is no exception. But how is AI used in healthcare?
The use of AI in healthcare has the potential to revolutionize diagnostics, treatment planning, patient care, and more. As AI becomes increasingly integral to healthcare, it’s crucial for healthcare professionals and key decision-makers to understand how to effectively evaluate and choose AI solutions that will have a positive impact on patients and providers.
Understanding AI and its Applications in Healthcare
The Oxford Dictionary defines artificial intelligence as “the theory and development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages.” This definition applies to AI technology as a whole; however, not all AI is created equal.
There are several types of AI, with each type offering a specific range of functions that can address various issues. A few common types of AI in healthcare include generative AI, assistive AI, and autonomous AI.
- Generative AI relies on human prompts to generate text, images, and other media. Generative AI technology has implications for a wide variety of industries and holds promise for applications in healthcare, such as automating routine tasks like responding to patient emails and transcribing discharge instructions and treatment plans. One example of generative AI in healthcare is Abridge. Abridge is designed to summarize patient conversations into concise, accurate medical notes, reducing administrative burden on healthcare professionals. However, concerns around ethics, data security, accuracy, and reliability necessitate careful consideration regarding the technology’s implementation into the healthcare industry.
- Assistive AI is designed to augment human decision-making. In other words, it helps, or assists, humans in making better decisions, faster. In healthcare, assistive AI typically serves as a valuable support tool for medical professionals, aiding in tasks such as evaluating large datasets, taking measurements, and analyzing medical images. Paige.AI, for example, is an assistive AI designed for pathological analysis, assisting clinicians in cancer diagnosis. Essentially, assistive AI can act as a second set of eyes for clinicians, aiding in offloading certain tasks or enhancing back-office functions.
- Autonomous AI, which functions without direct human supervision, involves the technology making decisions on its own. Additionally, autonomous AI systems can be trained to consider a wide variety of potential outcomes to help reduce bias. As it relates to healthcare, autonomous AI applications are being used to provide medical diagnoses without the need for human interpretation. For example, Digital Diagnostics’ flagship product, LumineticsCore™, utilizes autonomous AI technology to diagnose diabetic retinopathy at the point-of-care, without physician oversight. LumineticsCore is designed to deliver ethically founded, reliable care and has been rigorously trained and validated to mitigate bias.
Glamour AI vs Impactful AI
As AI-powered healthcare solutions continue to evolve there are two terms that are worth exploring: glamour AI and impact AI.
Glamour AI refers to AI technology that focuses on developing technologically advanced solutions that may not address an existing need. The innovation may be highlighted for its potential rather than practical applications.
Impactful AI in contrast refers to technology solutions that are developed to directly address a known patient need and demonstrate tangible benefits.
At Digital Diagnostics, we strive to do AI the Right Way by developing impactful AI, such as LumineticsCore, which enhances diabetic retinopathy testing by bringing high-quality AI powered diagnostics to the point-of-care. Our technology not only streamlines the diagnostic process but can also help improve accessibility, addressing a critical need in the management of diabetes-related eye care.
The Impact of AI on Healthcare
While each type of AI addresses specific issues, collectively, AI is beginning to transform various aspects of healthcare for the better. AI technology has the capability to enhance medical professionals’ efficiency by reducing administrative burden and physician burnout, thus allowing clinicians to focus more on patient care and operate at the top of their license. AI can also help improve patients’ access to care, particularly in rural or underserved areas. AI-driven solutions can also help enable early disease detection, a significant advancement that can potentially improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. While still evolving, the profound impact AI is having on the healthcare industry is undeniable.
Importance of Choosing the Right AI
Choosing the right AI solution is crucial in healthcare settings, as misaligned technology can significantly disrupt workflows, placing additional burdens on healthcare professionals and adversely affecting patient care. Effective AI solutions should be designed to seamlessly integrate into existing healthcare workflows, enhancing efficiency without introducing burdensome complexities. This requires a meticulous evaluation process to ensure that the AI technology not only aligns with current practices but also demonstrates evidence-based effectiveness and promotes long-term sustainability.
At Digital Diagnostics thoughtful integration is always prioritized, starting with validating our technology in the intended clinical workflow to provide the least amount of disruption for providers. We continue to prioritize successful integration and ongoing use of LumineticsCore through designated Customer Success Representatives who are specially trained to facilitate the seamless implementation of our system into clinical workflow.
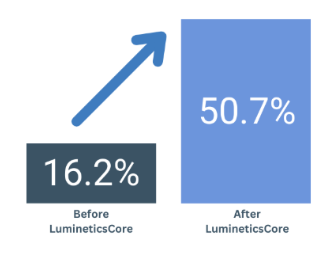
This is evidenced by notable enhancements in clinical outcomes for clinics that have implemented LumineticsCore. At John’s Creek Primary Care, the integration of LumineticsCore significantly boosted adherence rates for diabetic retinal exams from 16.2% to 50.7% based on a year-over- year data comparison.
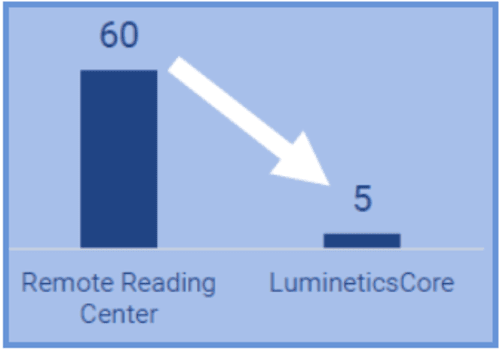
Similarly, at Tarzana Treatment Centers, the adoption of LumineticsCore not only improved the rates of annual eye exams for diabetes, which increased up to 71%, but also significantly reduced the time-to-follow-up. With LumineticsCore, the follow-up time decreased from 60 days, as experienced with a remote reading network, to just 5 days with the autonomous AI solution.
Conclusion
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly prevalent in healthcare, its ability to revolutionize the industry continues to expand. However, to truly harness this potential, it is up to healthcare professionals to shepherd the thoughtful incorporation of AI, carefully selecting technologies that not only integrate seamlessly into existing workflows but also deliver measurable, impactful results.
To learn more about the successful integration of LumineticsCore into healthcare workflows across the country, click here.